ASC2025 TEST_0_CONCURRENCY
How to find the bugs in the program
reference: https://nj.gitbooks.io/c/content/content/chapter10/chapter10-chinese.html
parallel problem bugs
unnecessary block
- dead lock
- live lock(condition not met)
- I/O block
conditional competition
- data race
- destroy constant
- life circle issues
how to find bugs
- read codes
- set breakpoint
- use tools
how did I find bugs in the pro
below steps are tying to test a progect when i didn't know if there were bugs.
step1: try to run the code and monitor the output
We can compile the code to a executable file by the instruction in the terminal, just a try.
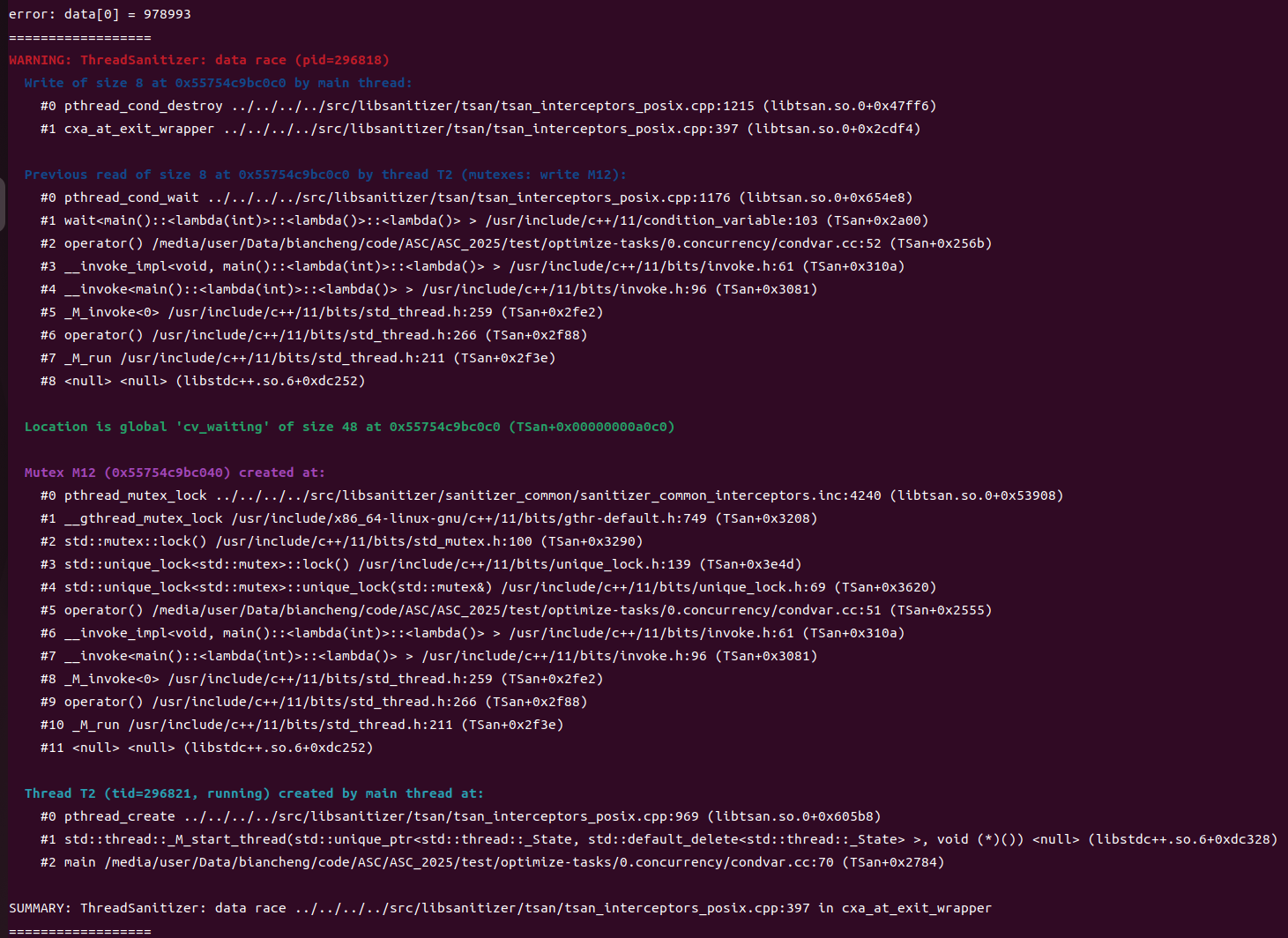
gcc condvar.cc -o try -pthread -lstdc++then run "try", the output is "error: data[0] = 718613".
so we can confirm there are some bugs in the codes, then try to find them.
we need to use some tools, such as ThreadSanitizer, to confirm the specific issue type.
g++ condvar.cc -fsanitize=thread -fPIE -pie -g -o TSanthen run the "TSan"
the output is "WARNING: ThreadSanitizer: data race (pid=30965)". so we can confirm there exist "data race" issue. then read codes to try to find if not "join()" or "condition variable" are here.
step2: read the codes and understand the brief frame
- "create_func" is a lambda expression and define the tasks of each thread.
- wait "m_waiting" to start work
- fetch a task, decrease the waiting task count
- thread of array position += 1
- one thread finish the task then notify the main thread by "notify_one()"
- the first "for circle" is set to creat the threads
- the second "for circle" is set to finish the main thread's task
- update the waiting task count and notify all threads to start working
- wait for all threads to finish and clear the finished task count, enter the next round
- the last "for circle" is set to check.
step3: set some log information
if we are back to the step1, you will find seem "warning" is after the data check, meaning we can't find the data error, so we must set some log information.
I choice to set the below codes.
// run 1000000 rounds
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
// update the waiting task count
lock lk_waiting(m_waiting);
waiting = 5;
std::fill(worktime.begin(), worktime.end(), true);
// notify all threads to start working
cv_waiting.notify_all();
lk_waiting.unlock();
// wait for all threads to finish
lock lk_finished(m_finished);
cv_finished.wait(lk_finished, []() { return finished == 5; });
// clear the finished task count, enter the next round
finished = 0;
lk_finished.unlock();
// log information
printf("finish %d %d %d %d %d %d\n", i, data[0], data[1], data[2], data[3], data[4]);
}after recompile and run it again, I found suprisely the five data sum up to 5000000, but one of them was not 1000000.
the answer is found out, threads of the task didn't work balancedly, some time some threads may work more than one time in one circle, so we just need to make sure just once.
how did I fix the bugs
step1: fix unbalanced work
I choice to introduce a new condition variable worktime for 5 threads, to make sure just work one time in one circle.
vec_t<bool> worktime (5, 0);then I add them into every threads as a judgement for starting to get work.
auto create_func = [](int tid) {
return [tid]() {
while (true) {
// wait for the signal to start working or exit
lock lk_waiting(m_waiting);
// add worktime
cv_waiting.wait(lk_waiting, [tid]() { return waiting > 0 && worktime[tid] || exit_flag.load(); });
if (exit_flag.load() && !worktime[tid]) {
break;
}
if (worktime[tid]) {
// fetch a task, decrease the waiting task count
waiting--;
worktime[tid] = false;
lk_waiting.unlock();
// do the work
data[tid] += 1;
// increase the finished task count
lock lk_finished(m_finished);
finished++;
cv_finished.notify_one();
lk_finished.unlock();
}
}
};
};and update the worktime at the beginning of every circle.
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
// update the waiting task count
lock lk_waiting(m_waiting);
waiting = 5;
//update the worktime
std::fill(worktime.begin(), worktime.end(), true);
// notify all threads to start working
cv_waiting.notify_all();
lk_waiting.unlock();
// wait for all threads to finish
lock lk_finished(m_finished);
cv_finished.wait(lk_finished, []() { return finished == 5; });
// clear the finished task count, enter the next round
finished = 0;
lk_finished.unlock();
printf("finish %d %d %d %d %d %d\n", i, data[0], data[1], data[2], data[3], data[4]);
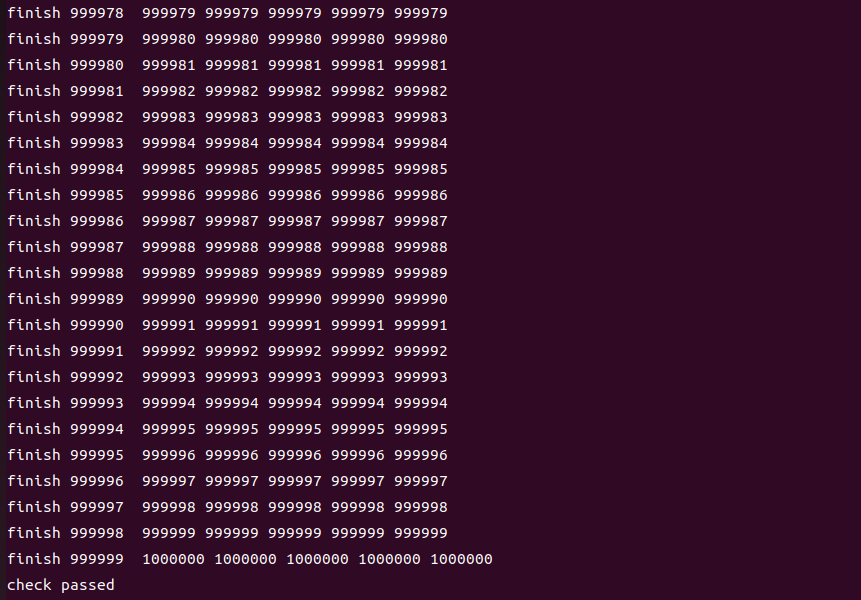
}then we can get check passed!
step2: exit sucessfully
this issue is easy to find out the reason, we can see it in the "WARNING: ThreadSanitizer: data race (pid=30965)".
By analysing the warning, we can easily find the issue occur when the main thread finished and try to destroy the global variables, but other threads are using them.
so we just need to use a variable to notify the thread to stop and use join() function to let main thread wait other threads.
// notify the thread to stop
exit_flag.store(true);
cv_waiting.notify_all();
// use join() to wait
for (auto &t : threads) {
if (t -> joinable()) {
t -> join();
}
delete t;
}then we can exit sucessfully!
check passed!
my answer
/*
* This task has 5 threads, each thread will increase the corresponding element
* in the data vector by 1. The main thread will run 1000000 rounds, in each
* round, it will notify all threads to start working, and wait for all threads
* to finish.
*
* After 1000000 rounds, the main thread will check if all elements in the
* data vector are 1000000.
*
* 1. Find the bug in the code, and fix it.
* 2. The code can bot exit normally, fix it, ensure all working threads are
* finished before the main thread exit.
*
*/
#include <condition_variable>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <mutex>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>
#include <atomic>
using std::mutex;
using std::thread;
using lock = std::unique_lock<std::mutex>;
using condvar_t = std::condition_variable;
template <typename T>
using vec_t = std::vector<T>;
mutex m_waiting;
mutex m_finished;
mutex m_workonce;
condvar_t cv_waiting;
condvar_t cv_finished;
condvar_t cv_workonce;
std::atomic<bool> exit_flag(false);
int waiting = 0;
int finished = 0;
// the data to be processed
vec_t<int> data(5, 0);
vec_t<bool> worktime (5, 0);
auto main() -> int {
vec_t<thread*> threads(5);
auto create_func = [](int tid) {
return [tid]() {
while (true) {
// wait for the signal to start working or exit
lock lk_waiting(m_waiting);
cv_waiting.wait(lk_waiting, [tid]() { return waiting > 0 && worktime[tid] || exit_flag.load(); });
if (exit_flag.load() && !worktime[tid]) {
break;
}
if (worktime[tid]) {
// fetch a task, decrease the waiting task count
waiting--;
worktime[tid] = false;
lk_waiting.unlock();
// do the work
data[tid] += 1;
// increase the finished task count
lock lk_finished(m_finished);
finished++;
cv_finished.notify_one();
lk_finished.unlock();
}
}
};
};
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
threads[i] = new thread(create_func(i));
}
// run 1000000 rounds
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
// update the waiting task count
lock lk_waiting(m_waiting);
waiting = 5;
std::fill(worktime.begin(), worktime.end(), true);
// notify all threads to start working
cv_waiting.notify_all();
lk_waiting.unlock();
// wait for all threads to finish
lock lk_finished(m_finished);
cv_finished.wait(lk_finished, []() { return finished == 5; });
// clear the finished task count, enter the next round
finished = 0;
lk_finished.unlock();
printf("finish %d %d %d %d %d %d\n", i, data[0], data[1], data[2], data[3], data[4]);
}
exit_flag.store(true);
cv_waiting.notify_all();
for (auto &t : threads) {
if (t -> joinable()) {
t -> join();
}
delete t;
}
// check, all element in data should be 1000000
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if (data[i] != 1000000) {
printf("error: data[%d] = %d\n", i, data[i]);
return 1;
}
}
printf("check passed\n");
return 0;
}